The 10 Warning Signs of Alzheimer's in 2024

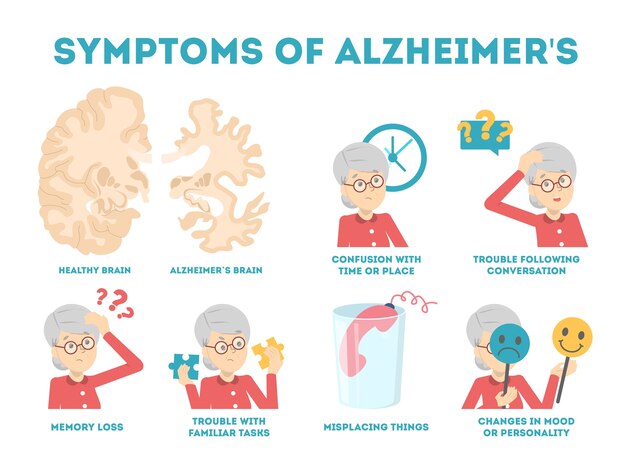
In 2024, it is crucial to be aware of the 10 warning signs of Alzheimer's disease. This neurodegenerative disorder affects millions of people worldwide, and early detection is essential for better management and treatment. The warning signs may include memory loss, difficulty completing familiar tasks, confusion with time or place, trouble understanding visual images or spatial relationships, new problems with words in speaking or writing, misplacing things and losing the ability to retrace steps, decreased or poor judgment, withdrawal from work or social activities, changes in mood and personality, and difficulty in planning or solving problems.
Recognizing these signs can prompt individuals to seek medical attention promptly, leading to timely interventions and support for both the patient and their families.
Understanding Alzheimer's: Causes, Symptoms, and Progression
Alzheimer's disease is a devastating and progressive brain disorder that affects millions of people around the world. As the most common form of dementia, Alzheimer's not only the individual diagnosed with the disease but also their loved ones and caregivers. It is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of Alzheimer's to better support those affected by it. This article aims to educate readers on the causes, symptoms, and progression of Alzheimer's disease.
Causes:
While the exact cause of Alzheimer's disease is still not fully understood, researchers believe that a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors contribute to its development. Age is the most significant risk factor, with most cases diagnosed in individuals over the age of 65. A family history of Alzheimer's also increases the likelihood of developing the disease. Certain genes, such as the APOE-e4 gene, have been linked to a higher risk of Alzheimer's. However, having these genes does not guarantee that an individual will develop the disease.
Symptoms:
Alzheimer's disease affects the brain, leading to a decline in memory, thinking, and reasoning skills. The symptoms may develop slowly and progress over time. Common early signs of Alzheimer's include difficulty remembering recent information, challenges in planning and problem-solving, confusion with time and place, and changes in mood and personality. As the health disease advances, individuals may experience severe memory loss, difficulty speaking, personal neglect, and an inability to recognize family members and friends.
Progression:
Alzheimer's disease follows a general pattern of progression, though the rate of progression can vary from person to person. In the early stage, individuals may experience mild memory loss and cognitive impairment, but can still perform daily activities independently. As the disease progresses to the middle stage, cognitive decline becomes more evident, and individuals require assistance with daily tasks. In the late stage, individuals become entirely dependent on others for their care, experiencing severe memory loss, impaired speech, and physical difficulties. The progression of Alzheimer's can span several years, with individuals requiring round-the-clock care in the final stages of the disease.
While there is no cure for Alzheimer's disease, early diagnosis plays a vital role in managing the symptoms and providing appropriate care. Medical professionals use a variety of assessments, including cognitive tests, brain imaging, and medical history evaluations, to diagnose Alzheimer's. Medications and therapeutic interventions can slow down the progression of symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with the disease.
Alzheimer's Prevention: Promoting Brain Health and Reducing Risk Factors

Alzheimer's disease is a devastating neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. As the population ages, the prevalence of Alzheimer's continues to increase, making it more important than ever to focus on prevention. While there is no surefire way to prevent Alzheimer's, there are steps you can take to promote brain health and reduce risk factors associated with the disease. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Engage in Regular Physical Exercise:
Exercise has long been known to benefit overall health, but it can also play a role in brain health and Alzheimer's prevention. Regular physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, promotes the growth of new neurons, and helps reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, which is a contributing factor to Alzheimer's. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or swimming, each week.
- Adopt a Healthy Diet:
What you eat can have a significant impact on your brain health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like those found in fish, nuts, and olive oil can help reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer's. Include foods that are high in antioxidants, such as berries, dark leafy greens, and colorful vegetables, as they can help protect brain cells from damage.
- Keep Your Mind Active:
Engaging in mentally stimulating activities can help keep your brain sharp and potentially decrease the risk of Alzheimer's. Reading, solving puzzles, learning a new skill, or playing strategy games are all examples of activities that can challenge your brain and promote cognitive health. Socializing with others is also important, as maintaining strong social connections has been linked to better brain function.
- Get Enough Sleep:
Sleep plays a vital role in overall brain health and the formation of memories. Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer's. Aim for seven to nine hours of quality sleep each night and establish a regular sleep routine to ensure optimal brain functioning.
- Manage Chronic Conditions:
Conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity have been linked to an increased risk of Alzheimer's. Take steps to manage these conditions through a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. This may involve making healthier food choices, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and taking prescribed medications to control blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
- Stay Mentally and Emotionally Healthy:
Chronic stress, depression, and social isolation can negatively impact brain health and increase the risk of cognitive decline. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as through exercise, relaxation techniques, or engaging in enjoyable activities. Seek support if you are dealing with depression, anxiety, or other mental health concerns, as addressing these issues can contribute to overall brain health.
While there are no guarantees when it comes to Alzheimer's prevention, adopting a brain-healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing the disease. By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can promote brain health, enhance cognitive function, and potentially protect yourself against the devastating effects of Alzheimer's. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, and taking care of your brain should be a top priority for a healthier future.